Better Sleep Starts Here: Proven Ways to Prevent and Treat Sleep Apnea
A good night’s sleep is essential for physical health, emotional balance, and mental clarity. Yet, for millions of people, restful sleep is interrupted by a condition known as sleep apnea—a disorder that causes repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. These interruptions can last from a few seconds to a minute or more and may occur dozens of times per night. Over time, untreated sleep apnea can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and chronic fatigue. The good news is that there are proven ways to prevent and manage this condition effectively, helping you achieve the deep, restorative sleep your body needs.
Understanding Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is broadly categorized into three main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), and complex sleep apnea syndrome.
Obstructive sleep apnea, the most common form, occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing a temporary blockage of the airway. Central sleep apnea, on the other hand, happens when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Complex sleep apnea is a combination of both types.
The symptoms of sleep apnea often go unnoticed by the person affected, as they usually occur during sleep. However, common warning signs include loud snoring, gasping for air during the night, morning headaches, daytime drowsiness, difficulty concentrating, and irritability. Partners often notice these symptoms first.
See also: Why Your Home Needs Basement Waterproof Coating
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
One of the most important steps in treating sleep apnea is recognizing it early. Many people dismiss snoring or fatigue as minor issues, but these can be indicators of a more serious problem. If you suspect you have sleep apnea, consult a healthcare provider or sleep specialist. They may recommend a sleep study to monitor your breathing patterns, heart rate, and oxygen levels overnight. Early diagnosis leads to quicker treatment and a reduced risk of long-term complications.
Why to Use a Sleep Apnea Test
Using a sleep apnea test is one of the most effective ways to identify whether you suffer from this common yet often overlooked sleep disorder. Many people experience symptoms like loud snoring, daytime fatigue, or morning headaches without realizing that interrupted breathing during sleep may be the cause. A sleep apnea test helps detect these breathing irregularities, providing valuable insights into your oxygen levels, sleep patterns, and overall sleep quality. Early diagnosis through testing allows for timely treatment, preventing serious health complications such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and diabetes. Whether you choose an in-lab study or an at home sleep apnea test, understanding your sleep health is the first step toward better rest and improved well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors
Multiple elements can play a role in the onset of sleep apnea. Excess body weight is one of the leading causes, as fat deposits around the upper airway can obstruct breathing. Age also plays a role—sleep apnea tends to be more common in middle-aged and older adults. Men are more likely to develop the condition than women, though risk increases for women after menopause.
Other risk factors include having a naturally narrow airway, nasal congestion, smoking, alcohol use, and certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes. Genetics can also
Proven Ways to Prevent Sleep Apnea
While not all cases can be prevented, there are several lifestyle changes that can significantly lower your risk of developing sleep apnea—or reduce its severity if you already have it.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess weight, especially around the neck, can increase pressure on the airway. Even modest weight loss can have a significant positive impact. Studies show that people who maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI) have a much lower risk of sleep apnea.
2. Avoid Alcohol and Sedatives
Alcohol and sedative medications relax the muscles in the throat, making airway obstruction more likely. Limiting or avoiding these substances before bedtime can help reduce breathing interruptions during sleep.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking causes inflammation and fluid retention in the airway, worsening sleep apnea symptoms. Quitting not only improves sleep quality but also enhances overall health.
4. Sleep on Your Side
Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and soft palate to collapse against the back of the throat, blocking airflow. Try sleeping on your side to keep your airway open. A supportive body pillow can help you stay in this sleeping position all night long.
5. Keep a Regular Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day supports your body’s natural sleep rhythm and may improve sleep quality. Consistency can make a significant difference for people prone to sleep apnea.
Effective Treatment Options
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, medical treatments can help manage sleep apnea and restore proper breathing during sleep. The right treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health.
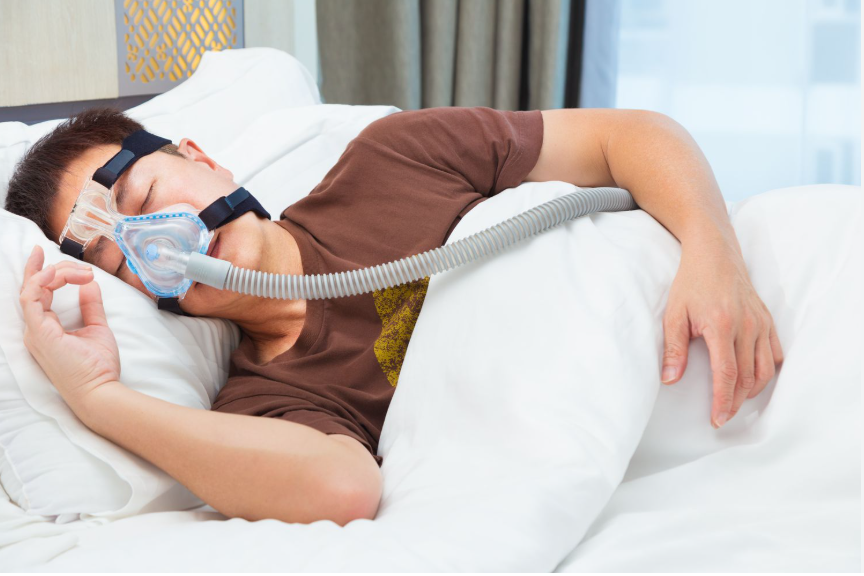
1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
The most common and effective treatment for obstructive sleep apnea is CPAP therapy. A CPAP machine delivers a constant flow of air through a mask, keeping the airway open. Though it may take time to get used to, CPAP is highly successful in preventing breathing interruptions and improving sleep quality.
2. Oral Appliances
For mild to moderate cases, dentists can fit oral appliances that reposition the jaw or tongue to keep the airway open. These devices are portable, quiet, and a good alternative for those who find CPAP uncomfortable.
3. Lifestyle and Behavioral Therapy
Weight loss programs, smoking cessation, and dietary changes can complement other treatments. Even a 10% reduction in body weight can significantly decrease the severity of sleep apnea.
4. Surgery
In severe cases where other treatments fail, surgical options may be recommended. Procedures can include removing excess tissue from the throat, repositioning the jaw, or implanting devices that stimulate airway muscles to prevent collapse.
5. Positional Therapy and Breathing Exercises
Special devices and exercises can help train you to sleep in positions that keep your airway open. Breathing exercises, such as those used in yoga or respiratory therapy, strengthen airway muscles and may reduce mild symptoms.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea can be life-altering, but it doesn’t have to control your nights—or your days. By adopting healthy habits, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and seeking professional treatment when needed, you can prevent and manage sleep apnea effectively. Better sleep starts with awareness, and the effort you put into improving your sleep health today will pay off in countless ways tomorrow.